Programme SoilMan
 |
 |
 |
| European Project (2017 - 2019) |
|
Context
|
Objectives
|
Study sites
|
Study parameters
|
Results
|
Partners
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Context
|
Soil biodiversity is pivotal for delivering food, fibre, biofuels, clean air, drinking water and carbon storage to society (Bardgett and van der Putten 2014). However, as stated by the European Commission Soil Thematic Strategy (COM2012/46), our understanding of how soil biodiversity is linked to soil functions and ecosystem services is still very limited (JRC 2012, Thiele-Bruhn et al. 2012, Lemanceau et al. 2014).
SoilMan is determined to work on a deeper understanding on the interrelationship between soil management, soil biodiversity, and ecosystem services. SoilMan brings together a broad spectrum of expertise in soil biology, soil science, ecology, and socio-economic sciences. A large number of both traditional and state-of-the-art methods and tools in soil ecosystem analysis as well as systematic economic and societal valuation of services provided by soil biodiversity will be applied. Via such an ecological, economic and political valuation of soil biodiversity in agricultural systems, soil biota will be placed into a socio-ecological context (cf. Pascual et al. 2015). No other ecosystems provide stronger interfaces between environmental responses to human activities and vice versa. In order to understand how farm-based soil management systems influence soil biodiversity and the sustainable provision of ecosystem goods and services, SoilMan will quantify soil ecosystem functions and multiple ecosystem services based on biodiversity parameters in typical mainstream agriculture in different European regions graded for the four basic soil management factors (1) tillage, (2) fertilization, (3) crop rotation, and (4) residue management. |
 |
Objectives
|
Objectives |
Workpackages (WP) |
|
|
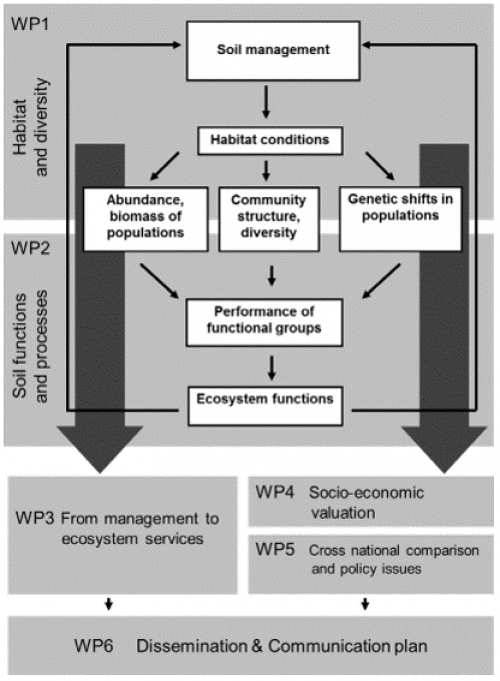
Objectives 1 - Explore European soil biodiversity as a function of land use characteristics and regional habitat conditions |
WP1: Habitat and Diversity |
 |
|
Objectives 2 - Explore the impact of soil biodiversity on soil functioning and the provision of soil related ecosystem services |
WP2: Soil functions and processes |
|
|
Objectives 3 - Develop a mechanistic model integrating biological activity in the soil and carbon dynamics |
WP3: From practices to services |
|
|
Objectives 4 - Value the most important goods and services soil biodiversity can provide for society and assess the impact of policy on its provision. |
WP4: Socio-economic valuation of services provided by soil organisms |
|
|
Objectives 5 - Compare the specific regional results and to link them with the European policies and laws debate in such a way that the results of SoilMan can be useful for policy and decision makers. |
WP5: Cross national comparison and policy issues |
Study sites
2017
| Country | Site - Studied practices | |
|
France |
 |
EFFEL -Tillage, Lusignan - Crop rotation |
|
Germany |
 |
Garte Süd - Tillage |
|
Romania |
 |
Turda - Tillage |
|
Spain |
 |
La Hampa - Tillage |
|
Sweden |
 |
Uppland - Tillage, Angermanland - Crop rotation |
Study biological parameters

Results
Dissemination activities
Scientific publications
- Bruns, T. D., Corradi, N., Redecker, D., Taylor, J. W., Öpik, M. (2017): Glomeromycotina: what is a species and why should we care? New Phytologist, doi: 10.1111/nph.14913.
- Lekberg, Y., Vasar, M., Bullington, L. S., Sepp, S.-K., Antunes, P. M., Bunn, R., Larkin, B.G., Öpik, M. (2018): More bang for the buck? Can arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities be characterized adequately alongside other fungi using general fungal primers? New Phytologist. doi: 10.1111/nph.15035.
Contributions to scientific conferences
-
Potthoff M., Pérès G., Taylor A., Scrader S., Landa B., Nicolai A., Sandor M., Öptik M., Guzmán G., Bergmann H., Cluzeau D., Banse M., Bengtsson J., Guernion M., Zaller J., Roslin T., Scheu S., Gómez Calero J-A., Schmoock I., Linsler D., and all collaborators (2017) Ecosystem services driven by the diversity of soil biota – understanding and management in agriculture, EGU, Austria, April 2017 (presentation).
- Schmoock, I., Linsler, D., Potthoff, M. (2017) Indicating resilience and sustainability in arable soil systems across Europe; Response of the soil microbial biomass to tillage reductions in four European countries. GfÖ, Ghent, Belgium, Dezember 2017 (poster).
- Potthoff, M. (2018) Ecosystem services driven by soil biota – understanding, valuation, and management, the SoilMan-Project. 6th Rhine-Waal Soil and Plant Ecology Seminar 2018, Kleve, Germany, February 2018 (presentation).
- Linsler, D. (2018) SoilMan: Soil biota responses to soil management – field sites conception and first results. 6th Rhine-Waal Soil and Plant Ecology Seminar 2018, Kleve, Germany, February 2018 (presentation).
- Beylich, A., Graefe, U. (2018) Tillage effects on enchytraeid diversity: Comparison of two field trials in Germany and Sweden, BONARES Conference, Berlin, Germany, February 2018 (poster).
- Torppa, K., Viketoft, M., Bengtsson, J. Taylor, A. (2018) Ploughing reduces earthworm abundance and bioturbation. OIKOS, Trondheim, Norway, February 2018 (poster).
- Langlais A., Hervé M., Nicolai A., Renault M. (2018) Services écosystémiques et évaluation des services environnementaux. Journée Interdisciplinaire : Gestion Durable des Ressources Naturelles et des Territoires, Rennes, February 2018.
- Schrader, S., Ludwig, M. (2018) Soil sustainability indicated and measured by soil resilience. EGU General Assembly, Vienna, Austria, April 2018 (presentation).
- Meyer-Wolfahrt, F., Oldenburg, E., Meiners, T., Munoz, K., Schrader, S. (2018) Farmers little helpers - Earthworms and collembolans potential role in pathogen repression and reduction of environmental contaminants. EGU General Assembly, Vienna, Austria, April 2018 (poster).
- Schmoock, I., Linsler, D., Potthoff, M. (2018) Indicating resilience and sustainability in arable soil systems across Europe. Response of soil microbial biomass to tillage reductions in three European countries. EGU General Assembly, Vienna, Austria, April 2018 (poster).
- Onica, B.-M., Dascalu, D., Stoian, V., Brad, T., Vidican, R., Sandor, M. (2018) Effects of tillage practices on the functional diversity of microbial community in arable soil. EGU General Assembly, Vienna, Austria, April 2018 (poster).
- Guzman, G., Montes-Borrego, M., Gramaje, D., Benitez, E., Gomez, J.A., Landa, B.B. (2018) Cover crops as bio-tools to keep biodiversity and quality in sloping olive orchards. EGU General Assembly, Vienna, Austria, April 2018 (poster).
- Nicolai A., Renault M. (2018) Ecosystem services driven by the diversity of soil biota (Biodiversa SoilMan). Atelier International: Hommes-Milieux, Rennes, May 2018.
Partners
Scientific partners
|
Estonia |
University of Tartu |
(UTAR) |
|
|
|
France |
INRA |
(INRA) |
|
|
|
Agrocampus Ouest |
(Agrocampus) |
|
|
|
|
University of Rennes 1 |
(UR1) |
|
|
|
|
Germany |
University of Göttingen |
(UGOE) |
|
|
|
Thünen-Institute |
(TI) |
|
|
|
|
Institute for Applied Soil Biology |
(IFAB) |
|
||
|
Spain |
Institute for Sustainable Agriculture, Spanish National Research Council. |
(CSIC) |
|
|
|
Sweden |
Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, NJ-faculty, Department of Ecology |
(SLU) |
|
|
|
Romania |
University of Agricultural Sciences and Veterinary Medicine Cluj-Napoca |
(UASVM) |
|
|






